Despite the widespread availability of graphical user interface (GUI) now-a-days, running commands on Linux through terminal is a common practice as this operating system (OS) is known to be used mostly by the tech-savvy folks. One may not say so when it comes to Windows where mouse-clicking is preferred by the general users, and admittedly, using command line interface (CLI) on Windows is sort of unwanted, if not scary; and therefore, avoided by most of the consumers. However, if you know the Windows run commands for the most common jobs, you can save your time to a great extent.
The following is a list of those simple commands (read the footnotes for more information):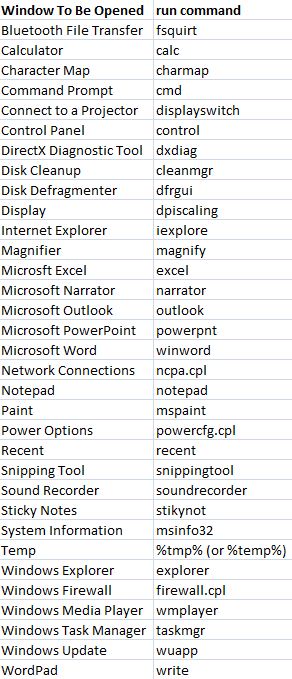
Character Map: To insert special signs and symbols.
Command Prompt: May be useful for, say, troubleshooting your internet connection when talking to the internet service provider.
DirectX Diagnostic Tool: Gives more info about your computer configuration than what is obtained when ‘Start’ button is left clicked, ‘Computer’ is right clicked, and ‘Properties’ is left clicked to ‘View basic information about your computer’.
Paint: Despite the appearance of ‘Snipping Tool’ for taking a screenshot with ease, ‘Paint’ may be still useful; for instance, ‘Snipping Tool’ cannot do it if you want to take a screenshot of a window having a drop-down list.
Recent: With this command, you open the directory of the recent files. Deleting these will help you save space, and keep system fast. Also, helps protect privacy.
System Information: Just like ‘DirectX Diagnostic Tool’.
Temp: With this command, you open the directory of the temporary files. Deleting these will help you save space, and keep system fast. Also, helps protect privacy. The ‘Recent’ and the ‘Temp’ commands do not delete your personal data like documents, music, pictures, videos and the other important info.
Windows Task Manager: You can also use the keyboard short-cut Ctrl + Shift + Esc.
Running these commands is straightforward. Hit Win + R to make the ‘Run’ window appear, type in the command, and hit ‘Enter’.
Remembering these commands would not be easy in the beginning; but, you will start recalling these in no time as these are the tasks you are likely to perform on regular basis.
I have tested the above commands in Windows 7 Professional 32 bit. These should work in the other Windows versions, too. All of the above commands can be run without the administrative privilege.
What are you waiting for? Start using these simple Windows run commands, and be productive at work, whether in home or at your office! Cheers!

 Email article
Email article