Let’s start this article with a story. A little while ago, when I turned on my PC, I noticed one of my backup drives had significantly less free space than it should have (approximately 50 GB of space unused space was not available). I didn’t understand how this space was missing because I had not saved any data to the drive since the last time I had turned my PC off. I checked all the files I had on the drive. The storage space used by the files was about 50 GB less than the total used space being reported on my drive. I ran the scan disk tool in Windows to see if there were any errors on the drive, noting none. So where did this 50 GB mysteriously go? I was stumped. I ended up getting frustrated, backed up my data to a different drive, and reformatted the seemingly corrupted drive. After reformatting the drive, it was back to normal.
Let’s start this article with a story. A little while ago, when I turned on my PC, I noticed one of my backup drives had significantly less free space than it should have (approximately 50 GB of space unused space was not available). I didn’t understand how this space was missing because I had not saved any data to the drive since the last time I had turned my PC off. I checked all the files I had on the drive. The storage space used by the files was about 50 GB less than the total used space being reported on my drive. I ran the scan disk tool in Windows to see if there were any errors on the drive, noting none. So where did this 50 GB mysteriously go? I was stumped. I ended up getting frustrated, backed up my data to a different drive, and reformatted the seemingly corrupted drive. After reformatting the drive, it was back to normal.
Fast forward into the future and something similar happened to me with another drive. This time I wasn’t about to flinch in the face of pure evil. Rather, I did some research and realized the “mysteriously disappearing space” is due to Shadow Copy Storage.
What Is Shadow Copy Storage?
Shadow Copy Storage is the place on your hard drives where shadow copies are stored by Volume Shadow Copy Service. Shadow copies may differ depending on the type of Windows you have but generally speaking, shadow copies are essentially System Restore points.
By default Windows sets aside 15% of total hard drive capacity or 30% of available free space for Shadow Copy Storage. You can check how much space is used by Shadow Copy Storage for your hard drives by:
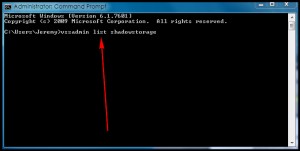
- Open Start Menu.
- Run Command Prompt. (Be sure to right-click and Run as Administrator if you are on Windows Vista/Win7.)
- Type vssadmin list shadowstorage…
…and hit Enter on your keyboard.
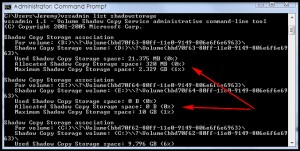
- After you hit Enter, Command Prompt will show how much how much Shadow Copy Storage space is currently being used, the amount of total space allocated to Shadow Copy Storage, and the maximum amount that can be allocated to Shadow Copy Storage for each of your hard drives:
(Typically you’ll see 15% of hard drive is the maximum amount that can be allowed to Shadow Copy Storage but in my case it is 1% because I have already reduced it.)
Reducing Shadow Copy Storage
As mentioned above, by default Shadow Copy Storage typically uses 15% of total hard drive capacity. Simply deleting System Restore points does not recover this hard drive space. The only way to recover this space is to reduce the amount of space consumed by Shadow Copy Storage.
To reduce the amount of space used by Shadow Copy Storage on your hard drives, do the following:
Note: This guide is for Windows Vista and Win7. Windows XP users can easily reduce the amount of space given to System Restore by right-clicking on My Computer -> Properties -> System Restore -> selecting a drive -> Settings -> moving the slider.
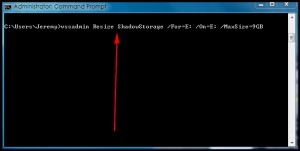
- Open Start Menu.
- Run Command Prompt. Be sure to right-click and Run as Administrator.
- In command prompt type vssadmin Resize ShadowStorage /For=[your hard disk]: /On=[your hard disk]: /MaxSize=[how much space you want to allocate] and hit Enter on your keyboard. For example, if I wanted to reduce Shadow Copy Storage on my E drive to a maximum of 9 GB, I’d type vssadmin Resize ShadowStorage /For=E: /On=E: /MaxSize=9GB:
Take note MaxSize can be in KB, MB, GB, TB, PB, or EB. Also note MaxSize should be set at 300MB or higher or else bad things will happen.
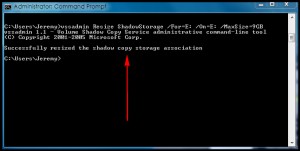
- After you hit Enter, you should get a message saying successfully re-sized the shadow copy storage association:
Repeat this process for all the hard drives which you want Shadow Copy Storage to be reduced.
Food For Thought
dotTechies should be aware that there are drawbacks for resizing Shadow Copy Storage. The obvious drawback is if you set Shadow Copy Storage too low then System Restore – and whatever else is using Shadow Copy Storage – won’t function properly. Another drawback is resizing Shadow Copy Storage may cause your current System Restore points to be deleted.
Generally speaking, with hard drives being so large nowadays, it is not a good idea to modify Shadow Copy Storage space on your main drive. If you insist on modifying on your main drive, be sure to give it enough space for System Restore to function properly. I leave mine at 7% of total capacity.
Conclusion
If you ever find yourself in a sticky HDD storage situation, reducing Shadow Copy Storage may be a potential solution. Is it the best solution? I don’t know. Shadow Copy Storage has been reworked and made leaner in Windows 8 because, according to Microsoft, it has a “negative impact on performance” and is not used often. So maybe we are justified in reducing Shadow Copy Storage. Or maybe we aren’t. Who truly knows. Whatever the case may be, I’d suggest keeping this tip in mind if you are in urgent need of extra storage capacity.
[First image credit: TheBankBall]

 Email article
Email article