Those who often use the MS Command Prompt can edit file attributes with it. For example, you can select attributes such as Hidden, Read-only and archiving for specific files by entering attribute switches in the Command Prompt. This is the basic syntax for editing file attributes via Command Prompt.
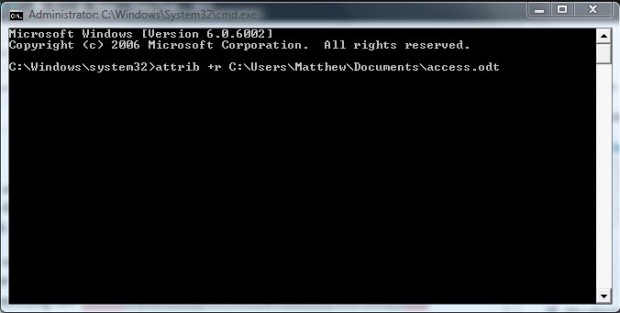
First, open the Command Prompt by entering cmd in the Start menu. Then right-click the cmd.exe and select Run as administrator from the context menu. That will open the Command Prompt window in the shot below.
To edit file attributes, you should enter attrib followed by some basic switches and then the path of the file. The three basic attrib switches are R, H and A. R assigns the Read-only attribute, H assigns the Hidden attrib and A prepares a file for archiving.
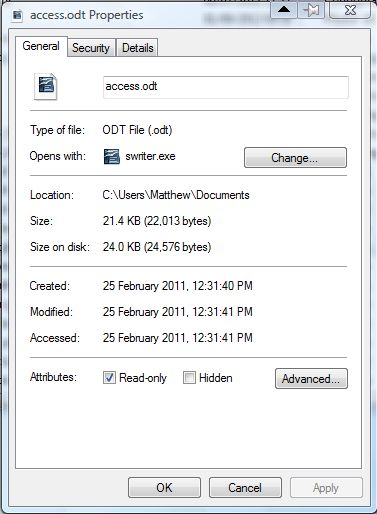
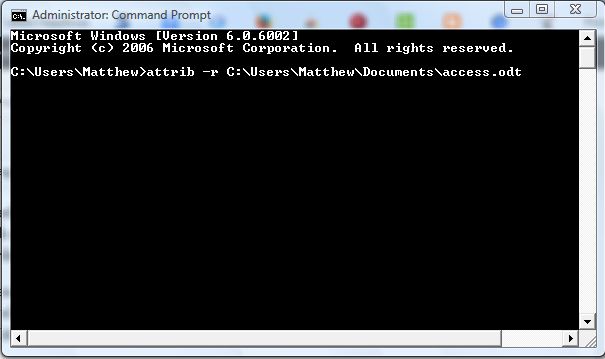
To select Read-only for a file, enter attrib +r [path] and press Return. Of course, you should enter the exact path of the file at the end of the line as in the shot below. So the line could be something like: attrib +r C:\Users\Matthew\Documents\access.odt.
Then right-click the file you selected the attribute for and select Properties. The Read-only check box on that window will then be selected as below.
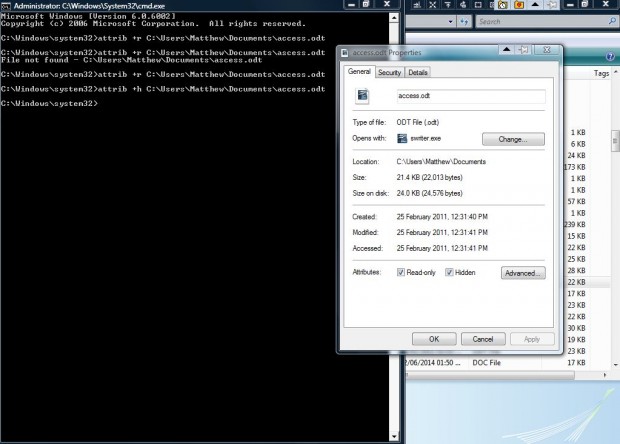
You can select the Hidden attribute on the Properties window much the same with the Command Prompt. Just enter attrib +h [path] and press the Return key. Then you’ll find the Hidden check box selected on the file’s Properties window.
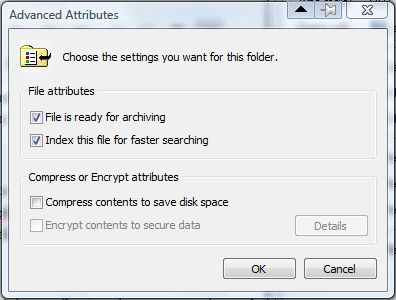
To select the File is ready for archiving attribute option, you must input the +a switch. As such, enter attrib +a [path] and press Return. That will then select the File is ready for archiving option shown in the shot below.
You can also deactivate those attribute options from the Command Prompt. Instead of entering +a or +h, replace the + with a -. So you would enter -a or -h to deactivate the specified attribute.
So now you can modify both file and folder attributes from the Command Prompt. Check out this page for further attrib command line details.

 Email article
Email article